Glutathione (Glutathione) is a potent antioxidant that plays a key role in cellular health, detoxification and immune function. However, due to its low bioavailability in the body, researchers and companies continue to explore innovative delivery systems to improve its absorption and efficacy. The following are some of the key innovations in today's glutathione delivery systems:
1. Liposomal Glutathione (LGG)
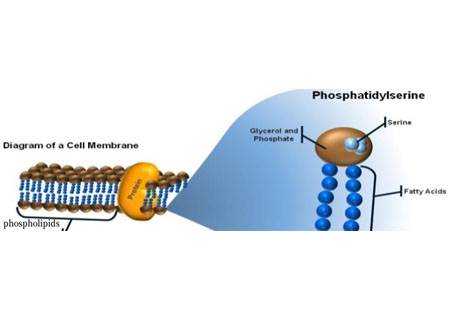
Liposomes are tiny vesicles encapsulated by a bilayer of phospholipids that protect the active ingredient from destruction by stomach acids and digestive enzymes. Advantages of Liposomal Glutathione are:
Higher bioavailability: liposome technology allows for more efficient cellular absorption than traditional oral supplements.
Longer in vivo circulation time: phospholipid encapsulation reduces the degradation of glutathione and improves its stability in the bloodstream.
2. Nanotechnology delivery systems (Nano-Glutathione)
The development of nanotechnology in the field of pharmaceuticals and nutritional supplements has driven the emergence of nano-glutathione. Its advantages include:
Higher cell permeability: the tiny size of nanoparticles makes it easier to penetrate cell membranes.
Improved glutathione stability: nano-encapsulation prevents glutathione degradation in the gastrointestinal environment.
3. Sustained-Release Glutathione (SRG)
Sustained-Release formulations prolong the duration of activity by controlling the release rate of glutathione so that it is released slowly in the body. This approach is particularly suitable for people who need to maintain antioxidant levels in the body for a long period of time, such as patients with chronic diseases or athletes.
4. Subcutaneous or intravenous injection (Injectable Glutathione)
Intravenous or subcutaneous injection of glutathione is a direct delivery method that bypasses the gastrointestinal tract and increases the concentration of glutathione in the blood. This method is commonly used for medical aesthetics, liver detoxification therapy, and patients with heavy antioxidant needs.
5. Precursor supplementation (Glutathione Precursors)
Due to the low direct oral absorption of glutathione, some studies have suggested supplementation with its precursors, such as N-acetylcysteine (NAC) or alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), in order to promote glutathione synthesis in the body. This strategy has been widely used in the field of antioxidant and immune support.
6. Transdermal Delivery (Transdermal Glutathione)
Transdermal patches or creams are able to absorb glutathione through the skin, avoiding degradation in the gastrointestinal tract while achieving a slow release effect. This method, although relatively poorly absorbed, provides an alternative for those who do not wish to take glutathione orally or by injection.